EE 570: Laboratory 3
Path Planning, Dynamics and Control
Due: Mo 05/04/2009
- Use the Newton-Euler algorithm to find the closed-form dynamic
equations for the planar, RP robot shown below. Assume
the links are symmetric about the center of mass,
so that only principal moments of inertia are present.
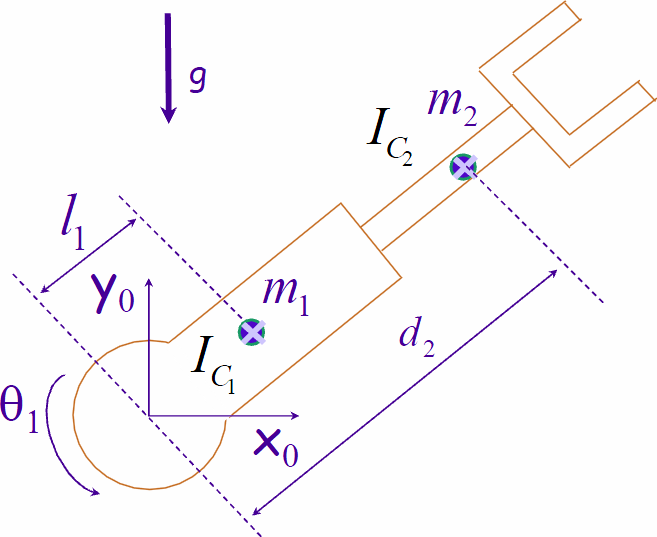
- Find the inertia tensor for each link given m1 = 5 kg, m2 = 4 kg, l1 = 0.4 m is half the length of link one, distance from link two's center of mass to either end is 0.5 m, and that links 1 and 2 can be represted as solid squares of width 10 cm and 8 cm, respectively.
- Generate smooth trajectories (with zero end velocities) for the end effector such that it moves from o2 = [-1.2, 1.2, 0] m to o2 = [0.8, 0.8, 0] m in 4 s.
- Use inverse kinematics to compute the joint variables and velocities that would yield the desired end-effector motion.
- Design and implement a controller from chapter 8 such that your robot tracks the joint variables determined from the inverse kinematics.
- Simulate your robot and controller using an ODE solver and demonstrate its performance in joint space and task (end-effector) space. You should also be able to visualize the movement.